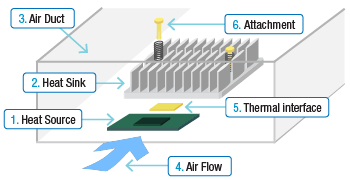
In order to properly select/design a heat sink,we need to clearly specify the operating conditions and calculate a thermal resistance target for the heat sink.
Please answer the following questions in as much detail as possible.
If you cannot answer a question, leave it blank, and we will fill in a typical value based on our experience.
After answering the questions, please push the "Request" button.We will review your responses and provide feedback ASAP.
Please fill in items 1 through 6, answering the questions as completely as possible.
If you are unsure about a question, leave it blank.
After completing all sections, press the "Request" button above to submit your information.
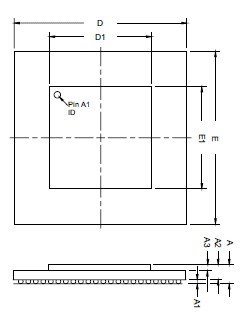
mm
mm
mm
°C
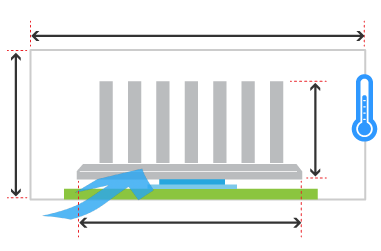
Heat Sink (L): mm
Wattage: W
Air Speed: m/s
| Company Name * | Department/Division |
|---|---|
| Country * | Name * |
| Email * | Phone # |
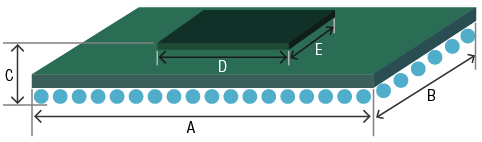
| A (mm) | B (mm) | C (mm) | D (mm) | E (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
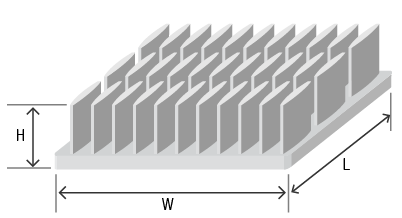
| W:Width(mm) | L:Length(mm) | H:Height(mm) |
|---|---|---|
A larger heat sink will typically perform better, as the surface area of the heat sink will become greater. Also, by increasing the volume of the heat sink, the amount of bypass area around the heat sink will be reduced, forcing more airflow to go through the heat sink.
However, a larger heat sink may require a more complicated and expensive attachment method. Push pins or shoulder screws versus thermal tape or epoxy. (REF:Online Catalog - Heat Sink Attachment)
If mechanical attachment hardware like push pins or shoulder screws are used, holes in the PCB must be located outside of the chip’s footprint. This will require the use of a larger heat sink or a heat sink with attachment tabs.
Close
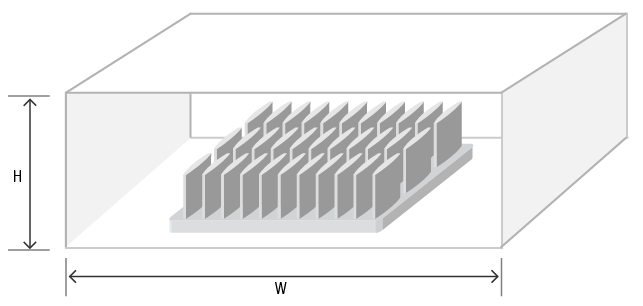
Has a formal duct been created to prevent air from bypassing around the heat sink? In the actual environment, if no duct has been created, other components like a daughter card, memory module, PCB components, the chassis, etc..., will act like a duct and help to channel the air. The estimated size of the duct created by these components is useful. If this detailed information is not available, just having height information for the chassis itself can be very useful.
| W:Width(mm) | H:Height(mm) |
|---|---|
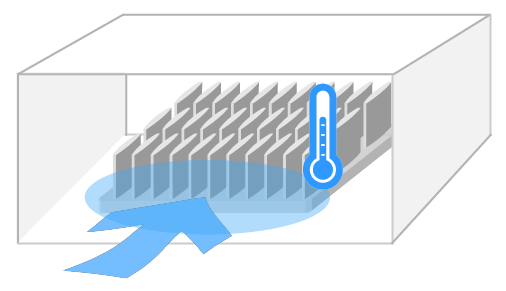
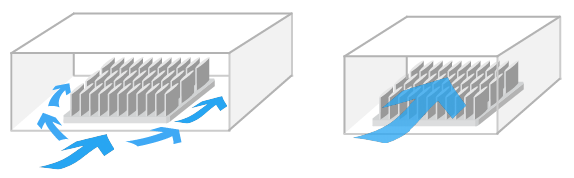
The air flow condition can be classified as Natural Convection or Forced convection.
Natural convection is a condition where the air flow is only generated by a a temperature differential and NOT by external means like a fan or blower.
Forced Convection is a condition where air flow IS generated by an external source like a fan or blower.
Greater air speed will result in better thermal performance.
In the actual environment, the air speed generated by a fan or blower will depend on many factors, such as where the components are located relative to the heat sinks, and fin pattern density of the heat sinks that are used.
The air speed used for simulation is ithe inlet air speed, just in front of the heat sink.
The following is a list of typical Alpha Standard TIM products. We carry many additional TIM products.
If you have requests, please input this information in the memo (Additional Information) section.
Thermal interface material(TIM) fills the small gaps and imperfections between the heat sink and heat source, minimizing the interface thermal resistance.
Please visit Online Catalog - Accessory - Thermal Interface Material.
If you choose adhesive tape for heat sink attachment, the adhesive tape itself is also the thermal interface material.
Pleaes visit Online Catalog - Accessory - Thermally conductive Adhesive Tape.
Generally, as the heat source size becomes smaller, the performance characteristics of the TIM becomes far more significant.
The heat sink attachment method is one of the most important factors regarding heat sink design. The method of heat sink attachment will have an impact on the selection of thermal interface material. For more details, please visit Online Catalog - Heat Sink Attachment.
| Company Name * | Department/Division |
|---|---|
| Country * | Name * |
| Email * | Tel |
| Additional Info | |